A good’s price elasticity of demand ( , PED) is a measure of how sensitive the quantity demanded is to its price. When the price rises, quantity demanded falls for almost any good, but it falls more for some than for others. The price elasticity gives the percentage change in quantity demanded when there is a one percent increase in price
Elasticity Survey Decide if you would purchase each of these items at the indicated price. If yes, raise your hand when told to do so. Keep track of. – ppt download
So once again, our change in quantity is plus 2, and our change in price is negative 1. And our elasticity of demand— change in quantity– 2 over average quantity, which is 17. Change in price is negative 1 over average price— 1 plus 2 divided by 2 is $1.50. Or $1.50 is right in between these two– divided by $1.50.

Source Image: fool.com
Download Image
Definition: Price elasticity of demand (PED) measures the responsiveness of demand after a change in price. Example of PED If price increases by 10% and demand for CDs fell by 20% Then PED = -20/10 = -2.0 If the price of petrol increased from 130p to 140p and demand fell from 10,000 units to 9,900 % change in Q.D = (-100/10,000) *100 = – 1%

Source Image: researchgate.net
Download Image
Segment 3: Pricing in Mass Markets
Transcript. Learn about the price elasticity of demand, a concept measuring how sensitive quantity is to price changes. Elasticity is calculated as percent change in quantity divided by percent change in price. Elastic situations have elasticity greater than 1, while inelastic situations have elasticity less than 1.
Source Image: studycorgi.com
Download Image
The Price Elasticity Of Demand Measures The
Transcript. Learn about the price elasticity of demand, a concept measuring how sensitive quantity is to price changes. Elasticity is calculated as percent change in quantity divided by percent change in price. Elastic situations have elasticity greater than 1, while inelastic situations have elasticity less than 1.
Price elasticity of demand (PED) measures the change in the demand for a product or service in response to a change in its price. With most goods, an increase in price leads to a decrease in demand – and a decrease in price leads to an increase in demand.
Elasticity of Demand: Definition, Types, Formulas | Free Essay Example
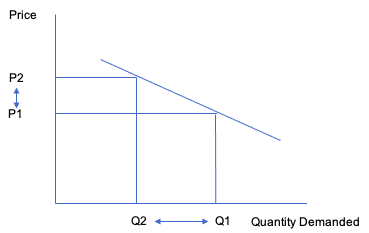
The price elasticity of demand is the ratio of the percentage change in quantity to the percentage change in price. As we will see, when computing elasticity at different points on a linear demand curve, the slope is constant—that is, it does not change—but the value for elasticity will change. Computing the Price Elasticity of Demand
Segment 3: Pricing in Mass Markets

Source Image: kwanghui.com
Download Image
Enotes World – ELASTICITY OF DEMAND: PRICE ELASTICITY… | Facebook
The price elasticity of demand is the ratio of the percentage change in quantity to the percentage change in price. As we will see, when computing elasticity at different points on a linear demand curve, the slope is constant—that is, it does not change—but the value for elasticity will change. Computing the Price Elasticity of Demand

Source Image: m.facebook.com
Download Image
Elasticity Survey Decide if you would purchase each of these items at the indicated price. If yes, raise your hand when told to do so. Keep track of. – ppt download
A good’s price elasticity of demand ( , PED) is a measure of how sensitive the quantity demanded is to its price. When the price rises, quantity demanded falls for almost any good, but it falls more for some than for others. The price elasticity gives the percentage change in quantity demanded when there is a one percent increase in price

Source Image: slideplayer.com
Download Image
Segment 3: Pricing in Mass Markets
Definition: Price elasticity of demand (PED) measures the responsiveness of demand after a change in price. Example of PED If price increases by 10% and demand for CDs fell by 20% Then PED = -20/10 = -2.0 If the price of petrol increased from 130p to 140p and demand fell from 10,000 units to 9,900 % change in Q.D = (-100/10,000) *100 = – 1%
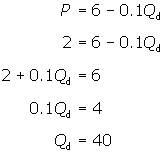
Source Image: kwanghui.com
Download Image
Measurement and Interpretation of Elasticities – ppt video online download
Price elasticity refers to how the quantity demanded or supplied of a good changes when its price changes. In other words, it measures how much people react to a change in the price of an item. Price elasticity of demand refers to how changes to price affect the quantity demanded of a good.

Source Image: slideplayer.com
Download Image
Economics Principles of N. Gregory Mankiw & Mohamed H. Rashwan – ppt download
Transcript. Learn about the price elasticity of demand, a concept measuring how sensitive quantity is to price changes. Elasticity is calculated as percent change in quantity divided by percent change in price. Elastic situations have elasticity greater than 1, while inelastic situations have elasticity less than 1.

Source Image: slideplayer.com
Download Image
Difference between Price Elasticity and Income Elasticity – Tutor’s Tips
Price elasticity of demand (PED) measures the change in the demand for a product or service in response to a change in its price. With most goods, an increase in price leads to a decrease in demand – and a decrease in price leads to an increase in demand.

Source Image: tutorstips.com
Download Image
Enotes World – ELASTICITY OF DEMAND: PRICE ELASTICITY… | Facebook
Difference between Price Elasticity and Income Elasticity – Tutor’s Tips
So once again, our change in quantity is plus 2, and our change in price is negative 1. And our elasticity of demand— change in quantity– 2 over average quantity, which is 17. Change in price is negative 1 over average price— 1 plus 2 divided by 2 is $1.50. Or $1.50 is right in between these two– divided by $1.50.
Segment 3: Pricing in Mass Markets Economics Principles of N. Gregory Mankiw & Mohamed H. Rashwan – ppt download
Price elasticity refers to how the quantity demanded or supplied of a good changes when its price changes. In other words, it measures how much people react to a change in the price of an item. Price elasticity of demand refers to how changes to price affect the quantity demanded of a good.